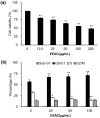
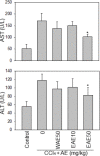
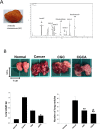
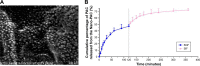
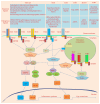
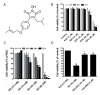
Microelements play pivotal roles for fungal/plant development and end-use properties. In this study, we examined the production and characterization of valuable sulfated polysaccharides (SPSs) with biological benefits from Antrodia cinnamomea and fine-tuning of mycelial culture conditions. Using various sulfated salts (e.g. CuSO4, FeSO4 and ZnSO4) to feed A. cinnamomea, we found that CuSO4 and ZnSO4 increased 25% and 20% of mycelium yields, respectively. We further isolated the SPSs from CuSO4, FeSO4 and ZnSO4-feeding of A. cinnamomea (called CuFSPS, FeFSPS and ZnFSPS, respectively) and found that CuSO4 and ZnSO4 significantly promoted SPS production. By contrast, FeSO4 did not change the yields of mycelium and SPS from A. cinnamomea. Characteristic studies have revealed that these sulfated salts did not significantly induce change in the sulfation and the sugar contents of SPS. However, the galactose and glucose contents in ZnFSPS were increased to the value of 249 and 1038 μmol/g, respectively. In addition, in regard to area percentages, while the major SPSs species were low-molecular-weight SPSs (<23 kDa), the sulfated salts increased the area percentages of molecular size in the range of 200-500 kDa. Anticancer function studies showed that those SPSs inhibit the cell viability 35-45% at 800 μg/ml of lung cancer A549 cells via downregulation of EGFR signaling. Our study is the first to identify the efficacy of microelements in the enhancement of mycelia yield and SPS, in which CuSO4 and ZnSO4 enhanced mycelia growth and increased the production of SPS. Our finding suggests that ZnSO4 may play roles in regulating the SPS assembling. Moreover, those SPSs derived from feeding A. cinnamomea with microelements may be useful as a potential agent for inhibition of lung cancer viability.
Health News
Antrodia cinnamomea is a polyporaceous medicinal and native fungus in Taiwan. In this study, we found that AC-SPS-F3, a sulfated glucan from A. cinnamomea, reduced lung cancer cell viability via inhibition of EGFR and mTOR activity. The co-administration of AC-SPS-F3 and cisplatin synergistically inhibited lung cancer cell viability. We identified AC-SPS-F3 was a sulfated β-(1→4)-d-glucan with two long 1,6-branches in each repeat unit. The FT-IR absorption at 1341 cm-1 and 887 cm-1 confirmed the existence of sulfates. The proposed repeat unit of AC-SPS-F3, including the types of main skeleton and side chains, as well as the position of the minor galactopyranosyl and mannopyranosyl residues, were proposed according to the 1D and 2D NMR spectra, shown as follows: The features for the proposed repeat unit of AC-SPS-F3 included two long β-(1→6)-Glcp branches, a very high ratio of sulfate substitution, and partial 2-O and 4-O substituents evenly distributed on the β-(1→6)-Glcp branches. The present study is first to characterize the highly branched sulfated polysaccharides and elucidates its anti-cancer functions.
Carbon and nitrogen sources in culture medium of Antrodia cinnamomea were optimized to eliminate the interference of exterior macromolecules on exopolysaccharide (EPS) yield by submerged fermentation. The results suggested that culture medium containing 50 g/L of glucose and 20 g/L of yeast extract as the optimal carbon and nitrogen sources could produce 1.03 g/L of exopolysaccharides. After purification, two heteropolysaccharides (AC-EPS1 and AC-EPS2) were obtained and characterized to provide the basic structure information. As the main component of the produced EPS, AC-EPS2 (accounting for 89.63%) was mainly composed of galactose (87.42%) with Mw (molecular weight) and R.M.S. (root-mean-square) radius of 1.18 × 105 g/mol and 25.3 nm, respectively. Furthermore, the spherical and flexible chain morphologies of EPS were observed in different solvents by TEM. The structural and morphological information of purified EPS were significant for further study on their structure-activity relationship and related applications.
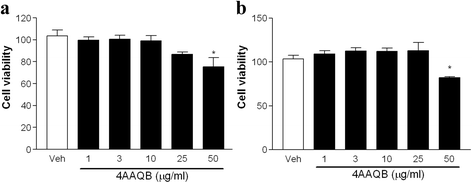
The functions of 4-acetylantroquinonol B (4-AAQB), a ubiquinone derivative isolated from the mycelium of Antrodia cinnamomea, in immunotherapy for liver cancer were investigated. We found that 4-AAQB could inhibit liver cancer stem cell related manifestations and activate the antitumor ability of dendritic cells. Specifically, 4-AAQB can inhibit EpCAM, AFP and related pathways of HepG2 cells. It also significantly decreases the expression of β-catenin, inhibits the tumorigenicity and decreases the secretion of immune escape related cytokines. Moreover, 4-AAQB can stimulate the proliferation of immune cells and promote the endocytosis of immature dendritic cells. When co-cultured immature dendritic cells with EpCAM+ HepG2 cells, 4-AAQB enhanced the expression of MHC class I and II on the surface of liver cancer stem cells and dendritic cells, increased the expression of costimulatory molecules CD80 of dendritic cells and cytokines related to immune activation. In conclusion, 4-AAQB from Antrodia cinnamomea can enhance immune function of dendritic cells against liver cancer stem cells, and may have the potential to be used for liver cancer prevention and immunotherapy.
We identified increased β-catenin and Atk expression was associated with drug resistance and poor prognosis in breast cancer patients using public databases. Antrocin treatment suppressed breast tumorigenesis and stemness properties.
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) is a nuclear hormone receptor that transcriptionally regulates lipid metabolism and inflammation; therefore, PPARα agonists are promising agents to treat dyslipidemia and metabolic disorders. PPARα full agonists, such as fibrates, are effective anti-hypertriglyceride agents, but their use is limited by adverse side effects. Hence, the aim of this study was to identify small molecules that can activate PPARα while minimizing the adverse effects. Antrodia cinnamomea, a rare medical mushroom, has been used widely in Asian countries for the treatment of various diseases, including liver diseases. Antcin B, H and K (antcins) and ergostatrien-3β-ol (EK100) are bioactive compounds isolated from A. cinnamomea with anti-inflammatory actions. Antcins, ergostane-type triterpenoids, contain the polar head with carboxylate group and the sterol-based body. Here, we showed at the first time that sterol-based compounds, antcins, but not EK100, activate PPARα in a cell-based transactivation study. The in silico docking studies presented several significant molecular interactions of antcins, including Tyr314, and His440 in the ligand-binding domain of PPARα, and these interactions are required for helix 12 (H12) stabilization. We propose that PPARα activation activity of antcins is related to their binding mode which requires conventional H12 stabilization, and that antcins can be developed as safe selective PPARα modulators.
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection is associated with B cell lymphomas in humans. The latent membrane protein 1 (LMP-1) of EBV constitutively activates the JAK/STAT signaling pathway and contributes to the proliferation of EBV-infected primary human B lymphocytes. Thus, targeting LMP1-induced JAK/STAT signaling may prove effective in treating B-cell lymphomas. The extract of the fruiting body of Antrodia cinnamomea, has been reported to have cytotoxicity on blood cancer cells. Here, we report that the bioactivity of antcin H, an analog of the JAK2 inhibitor zhankuic acid A (ZAA), inhibits LMP1-induced JAK/STAT related signaling and induces lymphoma cell line apoptosis. Moreover, antcin H enhances low-dose methotrexate (MTX) cytotoxicity against lymphoma cells. Treatment of antcin H with low-dose MTX significantly suppressed tumor growth and prolonged the survival of tumor-bearing mice. Our findings indicate antcin H as a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of EBV-infected cancer cells.
Antrodan, a unique protein-bound polysaccharide derived from the fungal mycelia of Antrodia cinnamomea, has been reported to exhibit antitumor and anti-metastatic effects on Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells through direct action and immunomodulation in vitro. In this study, we investigated the combined treatment of antrodan with an anti-cancer drug-cisplatin-and its underlying molecular mechanisms of action in a mouse xenograft tumor model. C57BL/6 mice were implanted (s.c.) with LLCs for nine days, before administration with only antrodan (20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg; p.o.) daily, only cisplatin (1 mg/kg; i.p.) twice per week, or a combination of both for an additional 28 days. As expected, antrodan on its own significantly inhibited metastasis of lung and liver tissues, while treatment with cisplatin only merely inhibited metastasis of the liver. Antrodan exhibited efficient adjuvant therapy in combination with cisplatin, by inhibiting the activities of the plasma urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) and the liver matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), as well as by inhibiting the phosphorylation of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) in lung and liver tissues. In addition, antrodan effectively ameliorated cisplatin-induced kidney dysfunction when treated combinatorially, as evidenced by a decrease in cisplatin-induced blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels in plasma and in the level of p38 phosphorylation in the kidney. Mechanistically, the actions of antrodan on its own involved (i) reducing the activities of uPA and MMP-2 and -9 in plasma; (ii) reducing protein expression of MMP-2/9, and the phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs), c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs), and p38 in lung and liver tissues; and (iii) enhancing immune system functions resulting in the promotion of an anti-metastatic response through immunomodulation, by increasing interferon-γ (IFN-γ) levels and decreasing interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in plasma. These results demonstrated that antrodan provides a novel, complementary therapeutic strategy against cancer metastasis, by attenuating the activities of MMP-2 and -9 through the modulation of STAT3/MAPK/ERK/JNK signaling pathways, and of the host’s immune system.
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women and affects 1.38 million women worldwide per year. Antiestrogens such as tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor (ER) modulator, are widely used in clinics to treat ER-positive breast tumors. However, remissions of breast cancer are often followed by resistance to tamoxifen and disease relapse. Despite the increasing understanding of the resistance mechanisms, effective regimens for treating tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer are limited. Antrodia cinnamomea is a traditional medicinal mushroom native only to Taiwan. In this study, we aimed to examine in vitro effect of antrodia cinnamomea in the tamoxifen-resistant cancer.
Antrodia cinnamomea is an indigenous medicinal mushroom in Taiwan, commonly used for the treatment of cancers and inflammatory disorders. 4-acetylantroquinonol B (4AAQB) is one of the active component isolated from the mycelium of A. cinnamomea. However, whether 4AAQB exhibits anti-inflammatory effect is not clear.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the inhibitory activities of ethanolic extracts from Antrodia cinnamomea (EEAC) on lung cancer. Cell proliferation and cell cycle distribution were analyzed using (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) (MTT) assay and flow cytometry, respectively. Wound-healing assay, Western blotting, and a murine tumor model were separately used to examine cell migration, protein expression, and tumor repression. Our results showed that EEAC induced cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase resulting decreased cell viability in A549 cells. Moreover, EEAC up-regulated the growth-suppressing proteins, adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), p21 and p27, but down-regulated the growth-promoting proteins, protein kinase B (Akt), mammalian tarfet of rapamycin (mTOR), extracellular signal-regulating kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), retinoblastoma protein (Rb), cyclin E, and cyclin D1. EEAC also inhibited A549 cell migration and reduced expression of gelatinases. In addition, our data showed that tumor growth was suppressed after treatment with EEAC in a murine allograft tumor model. Some bioactive compounds from EEAC, such as cordycepin and zhankuic acid A, were demonstrated to reduce the protein expressions of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 and cyclin D1 in A549 cells. Furthermore, EEAC enhanced chemosensitivity of A549 to paclitaxel by reducing the protein levels of caveolin-1. Our data suggests that EEAC has the potential to be an adjuvant medicine for the treatment of lung cancer.
Antrodia cinnamomea (AC) is found with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory biological activities. In this study, we investigated the anti-hepatitis effect of the emulsified AC extract from RO water or supercritical fluid CO2 with ethanol co-solvent extract methods of AC preparations.
Skeletal muscle atrophy, the most characteristic feature of cancer cachexia, often occurs in patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Antrodia cinnamomea (AC) a widely used edible medical fungus, exhibits hepatoprotective, anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities. In this study, we investigated whether combined treatment with the ethonolic extract of AC ameliorates cachexia symptoms, especially muscle wasting, in lung tumor-bearing mice treated with chemotherapy. Our results revealed that gemcitabine and cisplatin-induced severe body weight loss and skeletal muscle atrophy in the mice with cancer were greatly attenuated after AC extract administration. The protection may be attributed to the inhibition of skeletal muscle proteolysis by suppressing myostatin and activin release, muscle wasting-related FoxO3/MuRF-1/MAFbx signaling, proteasomal enzyme activity, and pro-inflammatory cytokine production. A significant decrease in insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) expression and formation was observed in the atrophying muscle of the conventional chemotherapy treatment group (CGC), and this decrease was markedly reversed by AC treatment. Additionally, the anorexia, intestinal injury and dysfunction that occurred in the CGC group were mitigated by AC extract. Taken together, these results demonstrated that the AC extract has a protective effect against chemotherapy-induced muscle atrophy mainly by attenuating muscle proteolysis, pro-inflammatory cytokine production, and anorexia, and activating IGF-1-dependent protein synthesis.
Antrodia cinnamomea (AC) is a medicinal fungal species that has been widely used traditionally in Taiwan for the treatment of diverse health-related conditions including cancer. It possesses potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in addition to its ability to promote cancer cell death in several human tumors. Our aim was to improve the anticancer activity of AC in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) through its cocultivation with ginger aiming at tuning the active ingredients. HCC cell lines, Huh-7 and HepG2 were used to study the in vitro anticancer activity of the ethanolic extracts of AC (EAC) alone or after the cocultivation in presence of ginger (EACG). The results indicated that the cocultivation of AC with ginger significantly induced the production of important triterpenoids and EACG was significantly more potent than EAC in targeting HCC cell lines. EACG effectively inhibited cancer cells growth via the induction of cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and induction of apoptosis in Huh-7 and HepG2 cells as indicated by MTT assay, cell cycle analysis, Annexin V assay, and the activation of caspase-3. In addition, EACG modulated cyclin proteins expression and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways in favor of the inhibition of cancer cell survival. Taken together, the current study highlights an evidence that EACG is superior to EAC in targeting cancer cell survival and inducing apoptotic cell death in HCC. These findings support that EACG formula can serve as a potential candidate for HCC adjuvant therapy.
Nanoencapsulated triterpenoids from petri dish-cultured Antrodia cinnamomea (PAC) and its amelioration effects on reproductive function in diabetic rats were investigated.
Antrodia cinnamomea (AC), an edible fungus growing in Taiwan, has various health benefits. This study was designed to examine the potential inhibitory effects of AC oligosaccharides on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo. By trifluoroacetic acid degradation, two oligosaccharide products were prepared from AC polysaccharides at 90 °C (ACHO) or 25 °C (ACCO), which showed different oligosaccharide identities. Compared to ACCO, ACHO displayed better inhibitory effects on LPS-induced mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, TNF-α and MCP-1 in macrophage cells. Further, ACHO significantly suppressed the inflammation in lung tissues of LPS-injected C57BL/6 mice. The potential anti-inflammatory molecular mechanism may be associated with the promotion of protein O-GlcNAcylation, which further skewed toward the marked suppression of p38 and Akt phosphorylation. Our results suggest that the suppressive effect of AC oligosaccharides on inflammation may be an effective approach for the prevention of inflammation-related diseases.
The medicinal mushroom Antrodia cinnamomea has been used to treat cancer but its anti-angiogenic effects have not been studied in detail.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that can be initiated by excessive activation of endosomal toll-like receptors (TLRs), particularly TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9. Therefore, inhibitors of endosomal TLR activation are being investigated for their ability to treat this disease. The currently approved biological drugs adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, ustekinumab, ixekizumab, and secukizumab are antibodies against effector cytokines that participate in the initiation and development of psoriasis. Several immune modulatory oligonucleotides and small molecular weight compounds, including IMO-3100, IMO-8400, and CPG-52364, that block the interaction between endosomal TLRs and their ligands are under clinical investigation for their effectiveness in the treatment of psoriasis. In addition, several chemical compounds, including AS-2444697, PF-05387252, PF-05388169, PF-06650833, ML120B, and PHA-408, can inhibit TLR signaling. Although these compounds have demonstrated anti-inflammatory activity in animal models, their therapeutic potential for the treatment of psoriasis has not yet been tested. Recent studies demonstrated that natural compounds derived from plants, fungi, and bacteria, including mustard seed, Antrodia cinnamomea extract, curcumin, resveratrol, thiostrepton, azithromycin, and andrographolide, inhibited psoriasis-like inflammation induced by the TLR7 agonist imiquimod in animal models. These natural modulators employ different mechanisms to inhibit endosomal TLR activation and are administered via different routes. Therefore, they represent candidate psoriasis drugs and might lead to the development of new treatment options.
In the present study, we investigated the effects of antrodin C (ADC), a maleimide derivative isolated from mycelia of Antrodia cinnamomea, on high glucose (HG, 30 mM)-accelerated endothelial dysfunction in vitro. HG-induced cytotoxicity in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) was significantly ameliorated by ADC. In addition, treatment with ADC significantly prevented HG-induced senescence, growth arrest at the G1-S transition phase and apoptosis in HUVECs. Moreover, the increased level of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) under HG condition was significantly ameliorated by ADC. Further analysis revealed that ADC-mediated anti-oxidant effects were due to up-regulation of cellular anti-oxidant genes, such as HO-1 and NQO-1 via promotion of the transcriptional activity of Nrf2, which was further confirmed by the failure of ADC to protect HUVECs from HG-induced dysfunction under HO-1 inhibition or Nrf2 silencing. Furthermore, hyperosmotic glucose (HOG, 60 mM)-induced uncontrolled production of ROS, rapid apoptotic cell death and HUVEC injury were significantly prevented by ADC, whereas these preventive effects were barely observed in HO-1 inhibited or Nrf2 silenced cells. Taken together, these results suggest that ADC may represent a promising intervention in diabetic-associated cardiovascular diseases by activating the Nrf2-dependent cellular anti-oxidant defense system.