Effects of Taiwanofungus camphoratus on non-specific and specific immune activities in mice.
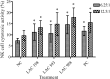
Taiwanofungus camphoratus is a precious medicinal fungus endemic to Taiwan and has been used as traditional medicine for a long time. Many pharmacological studies have revealed that T. camphoratus possessed various biological activities, such as immunomodulatory effects, anticancer activity and liver protective function. The aim of this study is to investigate the non-specific and antigen (ovalbumin [OVA])-specific immunomodulation effects of solid-state cultivated powder of T. camphoratus (Leader Antrodia cinnamomea [LAC]) in BABL/c male mice. In non-specific and antigen-specific immune function studies, 8-week-old mice were orally administered with LAC for 6 and 8 weeks, respectively. The results have shown that the proliferation of splenic immune cells, phagocytic activity of macrophages and cytolytic activity of natural killer cells were enhanced by LAC. Additionally, LAC increased the levels of IL-2, TNF-α, INF-γ, GM-CSF and serum OVA-IgG and OVA-IgM. These findings provided evidences that LAC had the immunomodulation effects on both antigen-specific and non-specific immune responses in mice.